Supplements & Vitamins
Showing 81–100 of 1582 results
-
BioLife Biotin 5mg 60 Capsules
N$150.00Biotin is an exceptionally powerful nutrient for the growth and strength of healthy hair and nails.
When Biotin is ingested, it reacts with cell enzymes and plays a vital part in producing amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Remember, hair itself consists of a protein called keratin. Consuming Biotin helps in the production of amino acids which are vital in the production of protein – keratin. Thus, it is clear that Biotin improves your hair’s keratin infrastructure.
When there is a sufficient amount Biotin in your body, you’re less likely to experience excessive hair fall because the essential vitamin important in the process of hair growth, will be abundantly available.
- Supports healthy hair
- Nail strength
- Hair growth
- Skin Wellness
Suggested use: Take one capsule daily, or as directed by your Health Professional.
Further information:
Ingredients: Biotin 5mg
Vegicaps
60 vegicaps 60 days
Bovine/ Porcine Free
Suitable for Diabetics
Preservative Free
Lactose Free
Gluten Free
No Artificial Flavours added -

BioLife Calcium Elemental 750g 60 Tablets
N$179.00Calcium plays an important role in bone health, as well as blood clotting and the proper functioning of the muscles, nerves, and heart functions.
Calcium is a crucial mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining the health of your bones and teeth, as well as facilitating various cellular functions throughout your body.
Further information:
Calcium plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the body, primarily due to its role as an essential mineral involved in cell signaling and muscle contraction. Here’s a detailed explanation of how calcium works in the body:
Cell Signaling: Calcium ions (Ca^2+) act as second messengers in cell signaling pathways. When a cell receives a signal, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter binding to a receptor on the cell membrane, it triggers a series of events that ultimately lead to an increase in intracellular calcium levels. This influx of calcium ions serves as a signal to activate or regulate various cellular processes, including gene expression, enzyme activity, and secretion of neurotransmitters or hormones.
Muscle Contraction: One of the most well-known functions of calcium is its role in muscle contraction. When a muscle receives a signal from a motor neuron to contract, it releases calcium ions from storage sites within specialized cellular structures called the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The influx of calcium ions into the muscle cell triggers a series of biochemical events that lead to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments, resulting in muscle contraction. Conversely, when the signal to contract is removed, calcium ions are actively pumped back into storage, leading to muscle relaxation.
Bone Health: Calcium is a primary component of bones and teeth, providing strength and structure. Throughout life, bone undergoes a continuous process of remodeling, where old bone tissue is broken down by cells called osteoclasts and new bone tissue is formed by cells called osteoblasts. Calcium, along with other minerals is deposited into the bone matrix during bone formation, helping to maintain bone density and strength. Adequate calcium intake, particularly during childhood and adolescence, is essential for building strong bones and reducing the risk of osteoporosis later in life.
Nerve Function: Calcium ions play a crucial role in transmitting nerve impulses throughout the body. When a nerve cell is stimulated, it undergoes a series of changes in membrane potential, leading to the opening of calcium channels and an influx of calcium ions into the cell. This influx of calcium ions triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the nerve terminal, allowing for communication between nerve cells and enabling various bodily functions, including movement, sensation, and organ function.
Overall, calcium is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of bones and teeth, regulating muscle contraction, facilitating nerve function, and supporting various biochemical processes throughout the body.
-

BioLife Co-Enzyme Q10 / 100mg 30 Capsules
N$159.00Known as “the body’s spark plug”, Coenzyme Q10 acts as a powerful antioxidant that plays a role in energy production and storage. It also neutralizes free radicals, preventing oxidative stress.
Coenzyme Q10 is a fat-soluble quinone that is produced naturally by the body. It is vital for producing energy within cells. Although our bodies are able to produce this powerful antioxidant, it can be found in various foods and is also available as a health supplement.
- Contributes to energy production.
- The ‘spark-plug’ antioxidant.
- Benefits cardiovascular system.
- May reduce symptoms of statin-induced myopathy.
- May boost physical performance and endurance.
Suggested use: Take one capsule daily, or as directed by your Health Professional
Further information:
Ingredients and supplement facts: Co-Enzym Q10 100mg – This product contains 1000 mg of Co-Enzyme Q10 in the form of ubiquinone. CoQ10 is found in almost every cell in the body, and acts as a powerful antioxidant that fights damaging particles in the body known as free radicals.
Ubiquinol vs. Ubiquinone
In our bodies, Coenzyme Q10 exists either in its oxidized form, ubiquinone, or in its reduced form, ubiquinol. Coenzyme Q10 shifts back and forth between its ubiquinone and its ubiquinol form in a continuous cycle inside the body depending on the body’s need. In the blood and lymph, Coenzyme Q10 primarily serves as an antioxidant. While in the mitochondria, it supports the energy metabolism by switching between the two forms back and forth many times per second. This is all part of Coenzyme Q10’s role in biology.
When you take a Coenzyme Q10 supplement in the form of ubiquinol, it changes to ubiquinone and vice versa.
When ubiquinone (the oxidized form) is used by the body, it transforms and becomes ubiquinol. Likewise, ubiquinol (the reduced form) becomes ubiquinone when it carries out its role in the body. So, when you take a Coenzyme Q10 supplement in the form of ubiquinol, it changes to ubiquinone and vice versa depending on the body’s need for either. This indicates that the one form, when encapsulated is by no means more superior to the other.
To better understand how this works, we’ll look at Coenzyme Q10 and cellular-energy production.
Every cell in the body has its own powerhouse, the mitochondria. Here, energy production occurs and this is where Coenzyme Q10 is found. In the process of energy production, electrons are exchanged between electron acceptors and donors.
Coenzyme Q10 acts as an electron acceptor or donor in the chain of reactions that lead to energy production. When oxidized Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone) accepts an electron from another molecule in the chain, it becomes reduced (ubiquinol). When reduced Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinol) donates an electron, it becomes oxidized (ubiquinone). Maintaining this balance is how your body most benefits from CoenzymeQ10.
Coenzyme Q10 is found in two forms:
Ubiquinol: The active antioxidant form.
Ubiquinone: The oxidized form.In general, enzymes receive the necessary support from coenzymes in order to carry out their various biochemical functions. It is present in all cells of the body, and is vital contributor to generating energy within cells. Coenzyme Q10 exists in higher concentrations in organs that require the most energy such as the kidneys, muscles, liver, and heart.
-

BioLife Joint Support 60 Tablets
N$215.00A specialised formula made of various ingredients, all of which may help reduce pain and inflammation and promote cartilage synthesis.
- Promotes Healthy Joints and connective tissues.
- Reduces pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints.
- Known to help with arthritis.
Suggested use: Take one or two tablets, once or twice daily, or as directed by your Health Professional.
Further information:
Acetyl.L.Carnitine – This product contains 500 mg of Acetyl-L-Carnitine in the form of HCL. ALCAR is highly bioavailable. It easily crosses the blood-brain barrier and delivers L-Carnitine across cell membranes.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin work in harmony to support healthy joints and connective tissues.
- Glucosamine is an important building block for healthy joints and connective tissues. It helps to support and strengthen collagen fibres, which are responsible for the strength and elasticity of your joints.
- Chondroitin is a type of carbohydrate that is found in your joints. It provides structural support and helps to keep your joints healthy and mobile. It also helps to keep your joints lubricated and comfortable. Together, Glucosamine and Chondroitin help to reduce pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is a painful condition that can affect the joints of your body. The pain can range from a mild ache to a severe sharp pain. Osteoarthritis affects the health of the cartilage in your joints. As the cartilage deteriorates, it can cause pain and swelling. This can lead to loss of motion and even joint damage. As the pain and swelling worsen, many people turn to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to ease their symptoms. These medications are safe and effective when taken appropriately. However, over time, frequent use of NSAIDs can cause stomach and intestinal damage, and may increase your risk of heart problems and stroke.
-

BioLife L-Lysine 1000mg 60 Tablets
N$149.00L-Lysine, an essential amino acid which may alleviate and/or reduce the duration and severity of painful shingles or cold sore outbreaks.
L-Lysine is one of nine essential amino acids in humans required for growth and tissue repair. Lysine is supplied by many foods, especially red meats, fish, and dairy products. L-Lysine seems to be active against herpes simplex viruses and may aid in the production of antibodies.
Lysine may help to slow down or prevent the growth of the Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1), which is responsible for causing Cold Sores / Fever Blisters. HSV-1 requires Arginine, which is another Amino Acid, to grow and replicate. Lysine helps prevent the body from absorbing Arginine, making it difficult for HSV-1 to grow and replicate.
- May alleviate the painful symptoms of shingles.
- Possesses an anti-herpes effect.
- Inhibits herpes.
- Plays a natural role in building connective tissue and healing wounds.
Suggested use: Take one tablet, three times a day for therapeutic use or one tablet daily for prophylactic use (as a preventative), or as directed by your Health Professional.
Further information:
L-Lysine 1000mg – This product contains 1000 mg of L-Lysine (HCL) in a vegan-friendly vegicap. Pregnant women should always consult with their doctor before taking this supplement.
Vegicaps
60 vegicaps 60 days
Bovine/ Porcine Free
suitable for vegetans
Suitable for Diabetics
Preservative Free
Lactose Free
Gluten Free
No Artificial Flavours added -

BioLife Milk Thistle Extract 375mg 60 Capsules
N$169.00Milk thistle is a powerful natural detoxifier, full of protective antioxidants, which work to neutralize toxins in your system and flush them out.
- Helps protect the liver from toxins.
- Stimulates cell regeneration in the kidneys and liver.
- Helps prevent gallstones and kidney stones.
Suggested use: Take 1 to 2 capsules daily, or as directed by your Health Professional.
-

BioLife Multivitamin +Anti-Oxidants 30 Capsules
N$145.00A unique, high-potency combination of essential vitamins, minerals, and anti-oxidants.
Biolife Multivitamin stands out not only for the abundance of nutrients it offers but also for the exceptional quality and potency of each ingredient. This formulation was designed to optimise the content every nutrient and to offer a high dose per nutritional ingredient.
This Multivitamin + Anti-Oxidant boasts an impressive array of over 27 essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Plus, not only does Biolife multivitamin deliver exceptional quality, but it’s also cost-effective, providing unbeatable value for the premium benefits it offers.
- Strengthen and maintain the immune system.
- Reduce the incidence of disease.
- Combat free radicals.
Suggested use: Take one capsule daily, or as directed by your Health Professional.
-

BioLife Vitamin B Complex 60 Capsules
N$169.00This Vitamin B Complex formula contains a high-potency combination of B vitamins, that gives a balanced boost of energy and may improve cognitive and immune system functions.
- Assists in energy production.
- Protects the nervous system.
- Essential for a healthy metabolism.
Suggested use: Take one capsule daily, or as directed by your Health Professional.
Further information:
Ingredients: Vitamin B Complex – This product contains a combination of B vitamins, in a vegetarian-friendly vegicap. These Vegicaps contain 7 different B vitamins, including the vital B12 as well as a powerful antioxidant; rooibos extract.
-

Biosil All In One Superfood 400ml Powder
N$153.00All-In-One Superfood Powder
Biosil All-In-One Superfood is a pure & powerful plant-based formula that may be taken to detox your body. This natural supplement contains all-natural ingredients: baobab powder, fulvic acid, diatomaceous earth, moringa and zeolite, that work together to increase nutrient absorption while decreasing inflammation and toxins in the body. Soothe and restore your body from within with Biosil All-In-One Superfood natural supplement.
- Anti inflammatory properties
- Bones and connective tissue improved
- Heavy metals, chemicals and toxin removal
- High blood pressure management
- Immune booster
- Nutrient absorption booster
- Skin, hair, nails restored
- Vitality boost
- Vitamins and minerals
- Free from fillers + preservatives
- Free from pesticides
- Free from lactose
- Suitable for vegans and strict vegetarians
-

Biosil All In One Superfood 180 Capsules
N$192.00All-In-One Superfood capsules
Biosil All-In-One Superfood capsules are a pure and powerful plant-based formula that may be taken to detox your body. This natural supplement contains all-natural ingredients: baobab powder, fulvic acid, diatomaceous earth, moringa and zeolite, that work together to increase nutrient absorption while decreasing inflammation and toxins in the body. Soothe and restore your body from within, with Biosil All-In-One Superfood natural supplement.
- Anti inflammatory properties
- Bones and connective tissue improved
- Heavy metals, chemicals and toxin removal
- High blood pressure management
- Immune booster
- Nutrient absorption booster
- Skin, hair, nails restored
- Vitality boost
- Vitamins and minerals
- Free from fillers + preservatives
- Free from pesticides
- Free from lactose
- Suitable for veans and strict vegetarians
-

Biosil Baobab 180 Capsules
N$267.00Baobab capsules
Biosil Baobab capsules consist of a natural superfood powder made from pure baobab fruit. Baobab fruit is high in Vitamin A & B6. It also contains vitamin C, bioflavonoids, calcium, magnesium, potassium, thiamine and zinc that all work together to support a healthy immune system. It’s believed to nourish your nerve endings and it also aids gut health and bowel regulation.
- 100% natural baobab powder
- An easy-to-serve and tasty superfood powder
- Citrus taste goes well with yoghurt, smoothies or just add to water
- Contains vitamin A, B6, & C
- Fibre, calcium, potassium & magnesium, potassium, thiamine, zinc & iron
- Slow-release energy
- Nourishes nerve endings
- Helps to support good gut health
- Promotes a healthy metabolism
- May give you more radiant skin
- May reduce fatigue and tiredness
- Helps you to feel more full & satisfied if added to food
- Can offer relief to diarrhea
- Naturally free from gluten
- No added sugar
- Non irradiated
- Additive free
- Suitable for vegans & vegetarians
-

Biosil Baobab 400ml Powder
N$103.50Baobab Powder
Biosil Baobab Powder is a natural superfood powder made from pure baobab fruit. Baobab fruit is high in Vitamin A & B6. It also contains vitamin C, bioflavonoids, calcium, magnesium, potassium, thiamine & zinc that all work together to support a healthy immune system. It’s believed to nourish your nerve endings & it also aids gut health & bowel regulation.
- 100% natural baobab powder
- An easy-to-serve & tasty superfood powder
- Citrus taste goes well with yoghurt, smoothies or just add to water
- Contains vitamin A, B6, & C
- Fibre, calcium, potassium & magnesium, potassium, thiamine, zinc & iron
- Slow-release energy
- Nourishes nerve endings
- Helps to support good gut health
- Promotes a healthy metabolism
- May give you more radiant skin
- May reduce fatigue & tiredness
- Helps you to feel more full & satisfied if added to food
- Can offer relief to diarrhea
- Naturally free from gluten
- No added sugar
- Non irradiated
- Additive free
- Suitable for vegans & vegetarians
-

Biosil Baobab 90 Capsules
N$159.00Baobab capsules
Biosil Baobab capsules consist of a natural superfood powder made from pure baobab fruit. Baobab fruit is high in Vitamin A & B6. It also contains vitamin C, bioflavonoids, calcium, magnesium, potassium, thiamine & zinc that all work together to support a healthy immune system. It’s believed to nourish your nerve endings & it also aids gut health & bowel regulation.
- 100% natural baobab powder
- An easy-to-serve & tasty superfood powder
- Citrus taste goes well with yoghurt, smoothies or just add to water
- Contains vitamin A, B6, & C
- Fibre, calcium, potassium & magnesium, potassium, thiamine, zinc & iron
- Slow-release energy
- Nourishes nerve endings
- Helps to support good gut health
- Promotes a healthy metabolism
- May give you more radiant skin
- May reduce fatigue & tiredness
- Helps you to feel more full & satisfied if added to food
- Can offer relief to diarrhea
- Naturally free from gluten
- No added sugar
- Non irradiated
- Additive free
- Suitable for vegans & vegetarians
-

Biosil Black Cumin 90 Capsules
N$136.50Black Cumin Capsules
Black Cumin (Nigella Sativa) is one of the most revered medicinal seeds in history.
Biosil Vegan capsules contain 100% pure black cumin seed powder. Please conduct your own research on this wonderful seed. There is a wealth of information available to this end. If it resonates with you, we have it right here for you.
- Assists with cancer
- Rheumatism
- Inflammatory conditions
- Asthma*
- Coughs*
- Enhances immunity*
*Black cumin seeds mixed with honey and garlic are excellent tonics for people with asthma or coughs as well as those who want to enhance their immunity during cold and flu season or when an infection is setting in.
-

Biosil Black Cumin Seeds 140g Seeds
N$144.00Black Cumin SeedsBlack Cumin (Nigella Sativa) is one of the most revered medicinal seeds in history.Please conduct your own research on this wonderful seed. There is a wealth of information available to this end. If it resonates with you, we have it right here for you.- Assists with cancer
- Rheumatism
- Inflammatory conditions
- Asthma*
- Coughs*
- Enhances immunity*
*Black cumin seeds mixed with honey and garlic are excellent tonics for people with asthma or coughs as well as those who want to enhance their immunity during cold and flu season or when an infection is setting in.
Further information:
Culinary uses
Black cumin seeds are small. They can be used to make tea by simply pouring hot water over the seeds and letting the brew steep for 10 minutes, about a tablespoon makes a nice cup of tea, but it is better to keep the cup covered until ready to drink so as to prevent the aroma from escaping.
The seeds can also be added to casseroles or breads, used in canning, or extracted in wine or vinegar. Some people grind the seeds and mix them with honey or sprinkle them on salads. They make a nice addition to salad dressings and even stir fry dishes, especially when combined with lemon, cilantro, and tahini. -
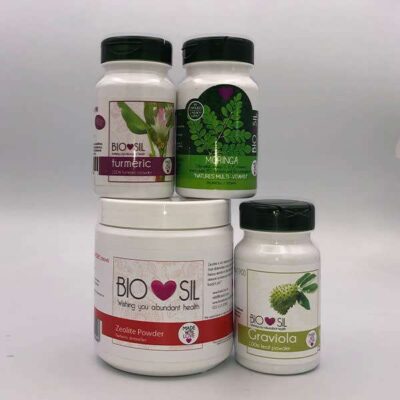

Biosil Cancer Combo Power Pack Turmeric Moringa Graviola Zeolite
N$655.50Cancer Combo
4 all natural power products. A powerful safe, natural alternative aid for helping to combat cancer.
- Graviola (soursop) 90 vegan capsules
- Moringa 90 vegan capsules
- Turmeric 90 vegan capsules
- Zeolite 500ml powder
Further information:
1. Graviola: an effective cancer remedy
2. Moringa: a superfood, health booster with a multitude of beneficial properties
3. Turmeric with added Piperine: a naturally powerful anti-cancer compound A derivative of turmeric, curcumin is the pigment responsible for turmeric’s yellow-orange colour. Every 100 grams of turmeric contains around 3 to 5 grams of curcumin, though turmeric is also very powerful on its own. New studies are shedding light on curcumin, and illuminating its numerous benefits on cancer and other diseases.
4. Zeolite: A natural mineral that absorbs and eliminates toxins, free radicals, and heavy metals from the body. It also boosts the immune system, without any side effects. It will help balance the body’s pH level. Foreign cells and free radicals can not survive in a balanced pH environment.
-

Biosil Charcoal Powder 200ml
N$94.50Activated Charcoal powder
A secret to naturally white teeth and many other health benefits. This product can be taken internally or used topically in compresses or for whitening teeth.
Suggested use: For a healing crisis, food poisoning, stomach issues or diarrhoea, take 1 teaspoon every hour until the symptoms begin to fade and then 2 x per day as required. Stir into a glass of water
Pets: This can also be given to cats and dogs
Activated charcoal is a bit particular about what it locks onto. It’s not interested in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, inorganic phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc and other compounds you probably want to keep, (including your tooth enamel). It does, however, happen to like tannins – the compounds found in coffee, tea (even herbal tea), blueberries, wine and spices like cinnamon that stain our teeth. As a bonus, activated charcoal also balances the mouth’s pH and is even considered beneficial enough to be used in some tooth re-mineralization formulas).
Important Note:
Activated charcoal does bind with iodine and may bind with other vitamins and minerals the body needs, so it is not usually recommended for internal use except when dealing with acute situations such as chemical or food poisoning. Activated charcoal does not work in situations where the material ingested is caustic, such as lye.
-

Biosil Chlorine Dioxide Solution 100ml
N$201.00CDS (Chlorine Dioxide Solution) Water and Body Purification Drops (200ml)
CDS is an already-activated form of MMS – Jim Humble’s formulation (Miracle Mineral Solution)
200 ml ready – to – use purification drops. Just add drops to a glass of water
- Purify your water
- add to all pets’ drinking water
Just as with MMS, this product may also be ingested orally.
Further information:
It should be noted that chlorine dioxide itself is an oxidizer, and not itself the “cure”. It effectively damages and eliminates harmful cells, cleansing the body of elements that are causing sickness, therefore allowing the body’s healthy cells to be able to do their jobs properly in helping the body to cleanse and heal itself.
The chlorine dioxide itself will not become toxic; it turns into regular table salt inside the body within 2 hours after consumption.
-

Biosil Diatomaceous Earth 90 Capsules
N$172.50Diatomaceous Earth Capsules
Pure, organic, food grade powder, natural and sundried, additive-free.
Benefits: When taken internally, many health benefits have been observed.
- Lower cholesterol
- Lower blood pressure
- Arthritis pain relief
- Increased energy
- More regular bowel movements
- Improved hair, skin and nails
- Sinus and cough relief
- Wonderful for your pets as well
-

Biosil Diatomaceous Earth Powder 500ml
N$107.00Diatomaceous Earth Powder
Pure, organic, food grade powder, natural and sundried, additive-free
When taken internally, many health benefits have been observed
- Lower cholesterol
- Lower blood pressure
- Arthritis pain relief
- Increased energy
- More regular bowel movements
- Improved hair, skin and nails
- Sinus and cough relief
- Wonderful for your pets
Further information and benefits:
Anti-aging, immune system booster, colon cleanser, parasite removalA daily supplement – it is estimated that there are more than 1,500 ways DE is beneficial to humans, plants, and animals.
As a daily supplement, many believe that its most beneficial use is for internal cleansing by aiding in the elimination of intestinal parasites, which are not able to develop immunity to the mechanical action of diatomaceous earth

